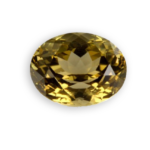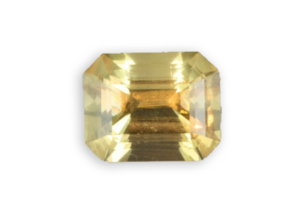
orthoclase

orthoclase crystals form Burma

adularia variety with adularescence phenomenon ( moonstone )

sanidine fancy cut

orthoclase from Mogok in Myanmar oval cut
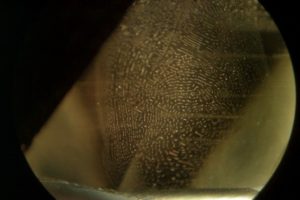
liquid type inclusions, healing fissure in fingerprint shape

solid like inclusions, ilmenite and rutile
Detailed sheet
orthoclase
Described by Breithaupt in 1823, its name comes from the Greek Greek “orthos” meaning “straight fracture“, because it has the characteristic to cleave in two orthogonal planes. Named at the beginning orthoclase, orthose, its french name, was given lately by René Just Haüy.
In its white variety adularia, which name comes from the Latin word “Adula” which was the name of Mount St Gothard in Switzerland where it was commonly found, it is a constituent of the moonstone. The adularia is actually a microperthite, a result of the demixing of microscopic platelets of albite in the orthoclase during the cooling of the mixture of orthoclase and albite.
The adularescence phenomenon, which is the apparition of bluish reflets, is due to the interference created by these micro-plates of albite in the orthoclase forming a real grating diffraction.
The sanidine is a light color variety (colorless, light brown), discovered by Nose in Germany in 1808, its name comes from the Greek “Sanis” which means “ in small plates “ and “Idos” for “ to see “, summarizing the appearance of its crystals.
It is the standard hardness number 6 on the Mohs scale of hardness which goes from 1 to 10 .

CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS
KAlSi3O8
potassium aluminum silicate

PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Main color
yellow
Other colors
brown, grey, colourless, pink, red, green
Color of streak
white
Luster
vitreous
Hardness
6.0 to 0.0
Density
2.55 to 2.65
Cleavage
perfect

OPTICAL PROPERTIES
Transparency
transparent
Refractive index
1.518 - 1.530
Double refraction
0.008
very weak, biaxial (-)
visible double refraction
No
Dispersion
0,012(0.008)
Pleochroism
very weak
Number of colors
2
colorless, yellow
Fluorescence
variable
orange - pink

CRYSTALS PROPERTIES
prismatic massive, often twinned for sanidine
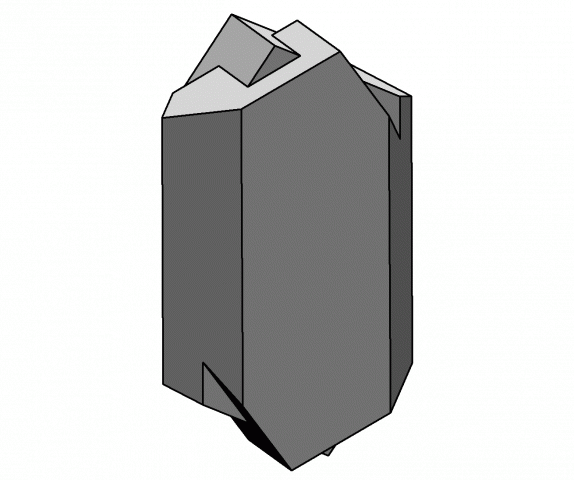
crystals system
monoclinic

OTHER INFORMATIONS

APPROACHING GEMS
Exploited
sites
Common feldspar, is found in Madagascar, Burma, Kenya, Mozambique, Rwanda, Namibia, Bolivia, India, Pakistan, China, Russia, Greece, Slovakia, Switzerland, France , England, North America, Australia
use in jewelry
It is used for emerald cuts type, or grading cut when the yellow color is quite strong.
Daily care
and precautions
Beautiful stone fairly easy to maintain, of medium hardness and therefore susceptible to scratches. It is washed with water and washing up liquid, rinse with water without lime and then with alcohol.
Historical
healing properties
As one of the constituents of the moonstone, it has some of its properties, it would be a smooth stone suitable for people too materialistic and rational, she would bring imagination, tolerance and sensitivity.
Venez visitez
notre site web
voillot-joaillier.fr
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec.